Cavities Dentist Perth
What are Cavities?

What are Cavities?
Cavities, also known as tooth decay or dental caries, are permanent holes that form in the surface of a tooth. They are caused by a combination of bacteria, food particles, and acids that gradually break down the enamel.
While cavities are common, they can lead to serious oral health problems if left untreated—such as tooth pain, infection, and even tooth loss. Early diagnosis and treatment can help preserve your natural teeth and prevent further complications.
At Genesis Dental in Canning Vale, we provide gentle, effective care to diagnose and treat cavities at every stage. Whether you’re experiencing discomfort or simply due for a check-up, our caring team is here to help keep your smile healthy.
Common Causes of Cavities
Cavities can form for a variety of reasons—some behavioural, others biological. Understanding the common causes can help you take proactive steps to protect your teeth.
Poor Oral Hygiene: Infrequent brushing and flossing allows plaque and bacteria to build up on the teeth.
Frequent Snacking or Sugary Drinks: Constant exposure to sugar feeds bacteria and leads to acid production, which erodes enamel.
Dry Mouth: A lack of saliva reduces your mouth’s ability to neutralise acids and wash away food particles.
Deep Pits and Grooves in Teeth: Natural tooth anatomy can trap plaque in hard-to-clean areas.
Worn Dental Work: Damaged fillings or crowns may create spaces where bacteria can thrive.
Diet Low in Nutrients: A diet lacking in calcium, phosphorus, and other minerals can weaken tooth enamel.
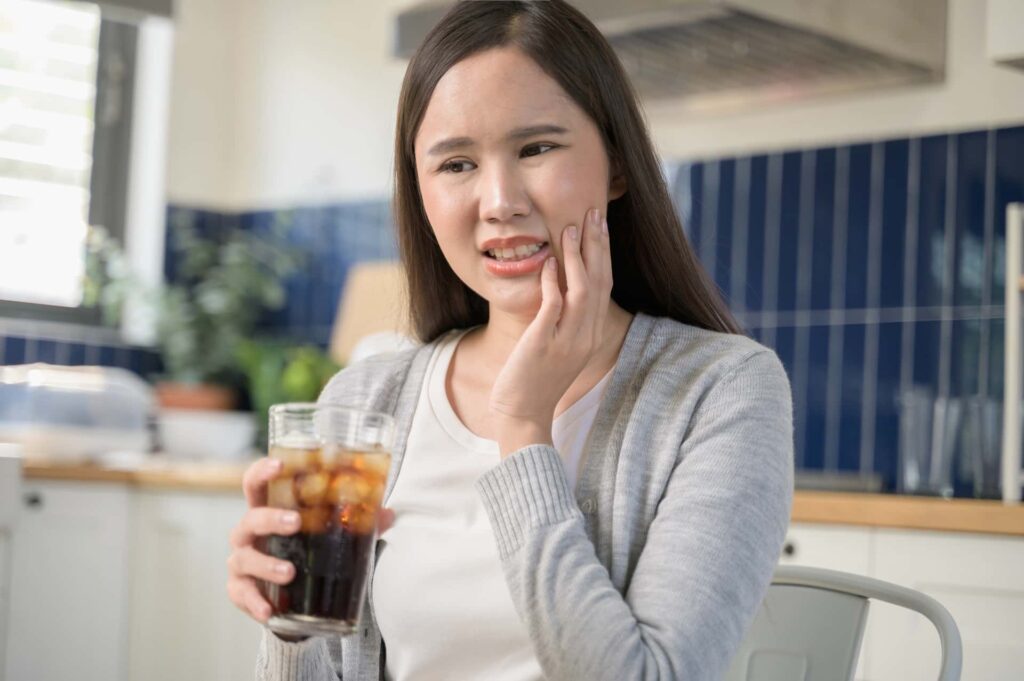
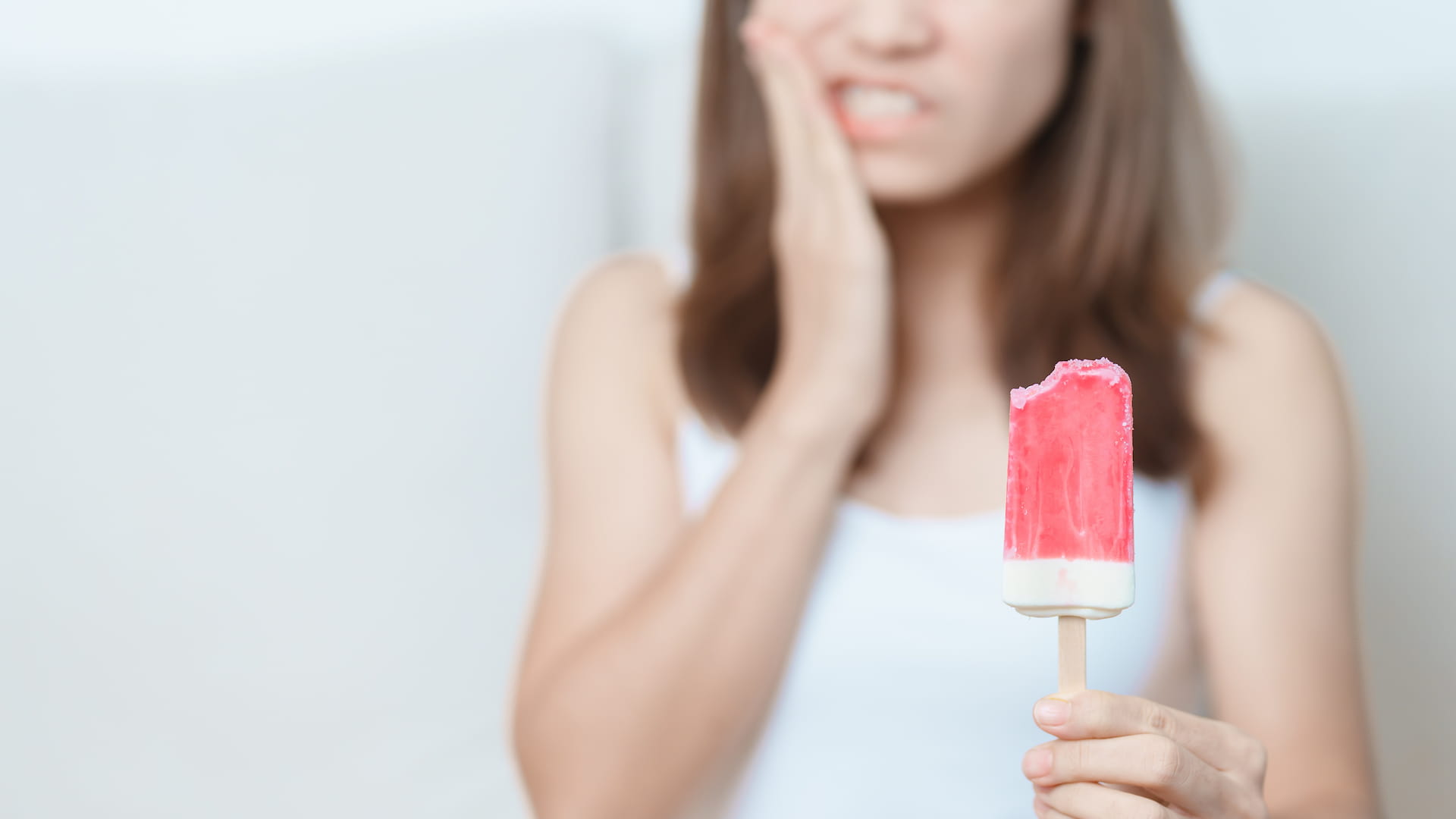


Symptoms of Cavities
Cavities don’t always cause pain right away, which is why regular dental checkups are so important. As decay progresses, you may begin to notice:
Toothache or Discomfort: Pain can range from mild sensitivity to sharp or throbbing pain.
Sensitivity to Hot, Cold, or Sweet Foods: Discomfort when eating or drinking may indicate enamel erosion or exposed dentin.
Visible Holes or Pits in Teeth: Cavities can sometimes be seen as dark spots or surface indentations.
Tooth Discolouration: A brown, black, or white spot on the tooth may be an early sign of decay.
Pain When Biting or Chewing: This may signal that the cavity has reached deeper layers of the tooth.
Persistent Bad Breath or Unpleasant Taste: Bacterial buildup from untreated cavities can cause noticeable odours.
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, early intervention can help prevent further damage.
Our Treatments for Cavities
At Genesis Dental, we offer tailored treatment options depending on the severity of the cavity and your overall oral health. Our goal is to restore your tooth’s strength, function, and appearance—while keeping you comfortable every step of the way.
Types of Cavities
Cavities can develop in different areas of the tooth and vary in severity. Identifying the type helps guide the most effective treatment:
Pit and Fissure Cavities:
These form in the deep grooves of the molars and premolars. They’re common in children and teens, and typically treated with fillings or fissure sealants.Smooth Surface Cavities:
Occur on the flat sides of the teeth, often between them. If detected early, they may be managed with fluoride treatment; more advanced decay may require fillings.Root Cavities:
These appear on the exposed roots of teeth, particularly in patients with gum recession. Root cavities can spread quickly and often require a filling or crown to restore strength.
If you suspect you may have a cavity, early assessment is key.
How To Prevent Cracked Teeth
Cavity prevention starts with healthy habits, regular checkups, and understanding your risk factors. Whether it’s deep grooves, exposed roots, or crowded teeth, certain areas are more prone to decay—but with the right care, cavities are often avoidable. Here are some ways to reduce your risk:
Brush Twice Daily with Fluoride Toothpaste:
Fluoride strengthens enamel and helps protect against decay on all surfaces of the teeth.Floss Every Day:
This helps remove plaque and food between teeth where smooth surface cavities can form.Limit Sugary and Acidic Foods:
Reduce snacking between meals and minimise sugary drinks that feed cavity-causing bacteria.Drink Plenty of Water:
Water helps wash away food particles and neutralise acids in the mouth—especially important for those with dry mouth.Schedule Regular Dental Checkups:
Routine exams help detect decay early, monitor changes, and apply preventive treatments where needed.Ask About Protective Treatments:
If you or your child is at higher risk of pit and fissure cavities, your dentist may recommend fissure sealants or topical fluoride applications for added protection.
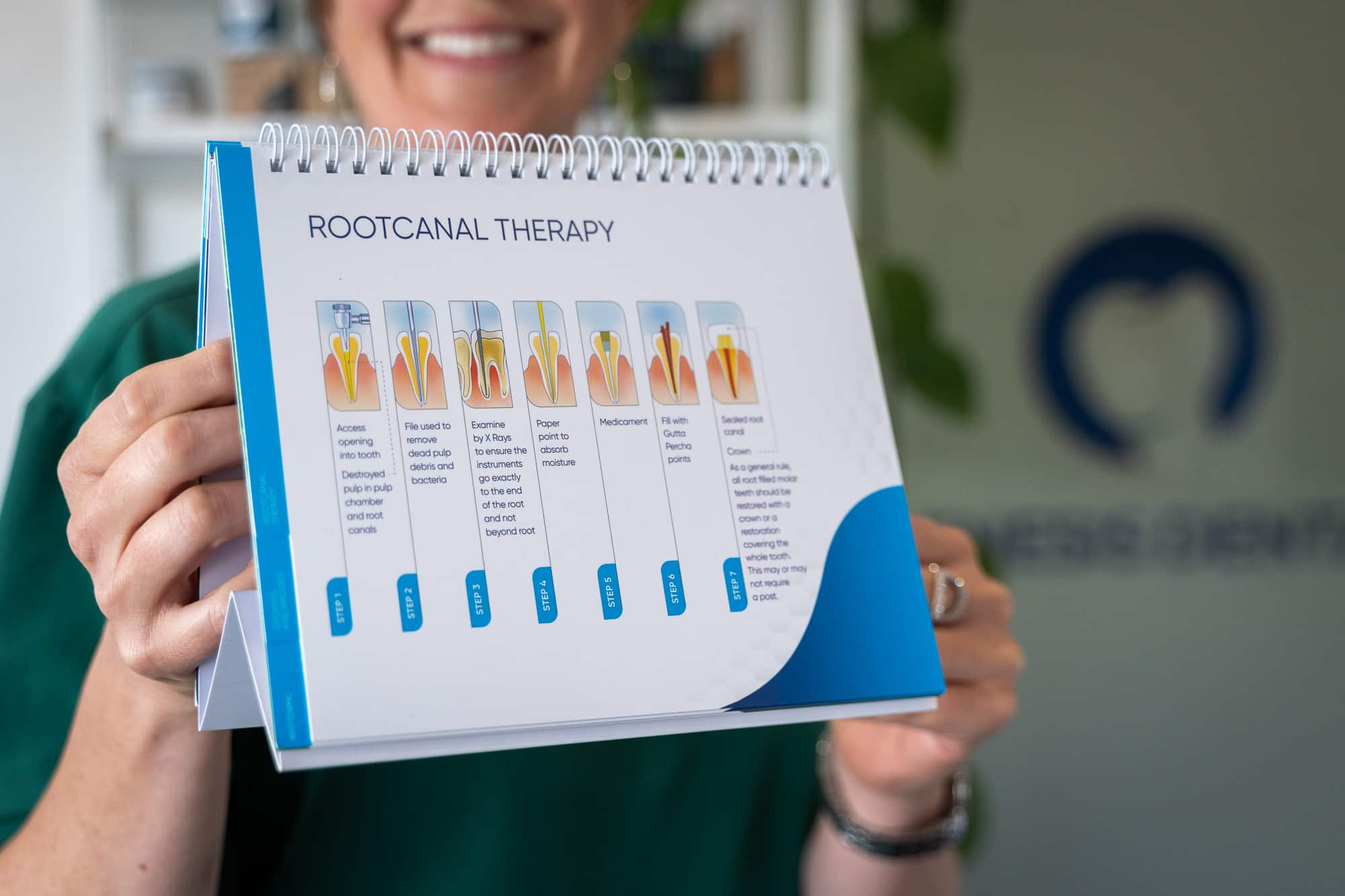

When Should I See a Dentist for Cavities?
You don’t need to wait for pain to seek help. Cavities often develop silently, and early treatment can prevent discomfort, infection, or tooth loss.
We recommend booking an appointment if you notice:
Sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods and drinks
Discomfort when chewing or biting
Visible holes or dark spots on your teeth
Ongoing bad breath or a bad taste in your mouth
A history of frequent cavities or enamel wear
Even without symptoms, regular checkups are essential to detect early decay and keep your oral health on track.
Associations
Our dentists are members of reputable dental associations, including the Australian Dental Association WA (ADAWA) and the Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Agency (AHPRA). We are also accredited by QIP, meaning our practice adheres to industry guidelines and regulations.
We accept all health funds, claimable on the spot for your convenience. We are preferred providers with HBF, HCF, CBHS and NIB, meaning you can maximise your rebate.
We also provide interest free payment plan options via The Tooth Market’s Fund My Dental. We also participate in government aided programs such as the Child Dental Benefits Scheme and provide top quality treatment for Department of Veterans’ Affairs (DVA) card holders.









Meet Our Team

Dr. Serene Ong
Dentist

Dr. Ben Luu
Dentist

Dr. Ashleigh Furfaro
Dentist

Dr. Amanda Lau
Dentist

Kelly Jones
Dental Assistant

Samantha St Johnston
Dental Assistant
Cavities FAQ's
Can a cavity go away on its own?
No. Once enamel is permanently damaged, the cavity won’t heal naturally. Early-stage demineralisation may be managed with fluoride, but actual cavities require treatment.
What happens if I ignore a cavity?
If left untreated, a cavity can worsen and lead to infection, severe pain, or tooth loss. Early treatment is quicker, easier, and less expensive.
How are cavities diagnosed?
Your dentist will examine your teeth visually and may use X-rays to detect decay between teeth or below the surface.
Do cavities always hurt?
Not always. Many cavities start painlessly, which is why regular dental checkups are so important for early detection.
Are children more at risk of cavities?
Yes. Children often have deep grooves in their molars and may struggle with consistent brushing, making them more susceptible to decay.
How can I reduce my child’s risk of cavities?
Encourage brushing with fluoride toothpaste, limit sugary snacks, and schedule regular visits to a family-friendly dentist.
Learn more about children’s dentistry
Contact Us
Contact our caring dentists in Canning Vale today with any questions about cavities or to book your consultation to start your journey to a healthy smile.